MCQs: Respiratory System. Part 1 of 2.
Click Here for the Notes on "Introduction to Respiratory System."
MCQs: Respiratory System. Part 1 of 2.
MCQs: Respiratory System. Part 1 of 2.
Quiz
Time for this test is 45 minutes.
- The physiological process involving movement of oxygen from the outside environment into the cell within tissues and transportation of carbon dioxide in the opposite direction is called ---
- Digestion.
- Respiration.
- Excretion.
- Metabolism.
- The branch of science that deals with the structure, function, diagnosis and treatment of diseases of lungs is called -----
- Pulmonology.
- Endocrinology.
- Neurology.
- ENT.
- Which of the following organs is common for Respiratory System and Digestive System?
- Nose (Nasal Cavity).
- Trachea.
- Pharynx.
- Larynx.
- Lungs.
- The process of moving air in and out of the lungs is called “-------”.
- Breathing.
- Digestion.
- Respiration.
- Pulmonary Ventilation.
- Inspiration, the phase of breathing when air -----.
- flows into the lungs.
- exit the lungs.
- Expiration, the phase of breathing when air -----.
- flows into the lungs.
- exit the lungs.
- The muscles that play major role in breathing are,
- Intercostal muscles and Diaphragm.
- Gluteus maximus muscle and Diaphragm.
- Intercostal muscles and Deltoid.
- Gluteus maximus muscle and Deltoid.
- Which of the following is wrong in case of “Inspiration”?
- Intercostal muscles contract.
- The ribs are pulled upward.
- Diaphragm contracts and moves downwards.
- It results in decreased “Lung Volume.”
- Which of the following is wrong in case of “Expiration”?
- Intercostal muscles relax
- The ribs come back to normal.
- Diaphragm relaxes and again forms its dome shape.
- It results in increased “Lung Volume.”
- The following diagram represents mechanism of ----
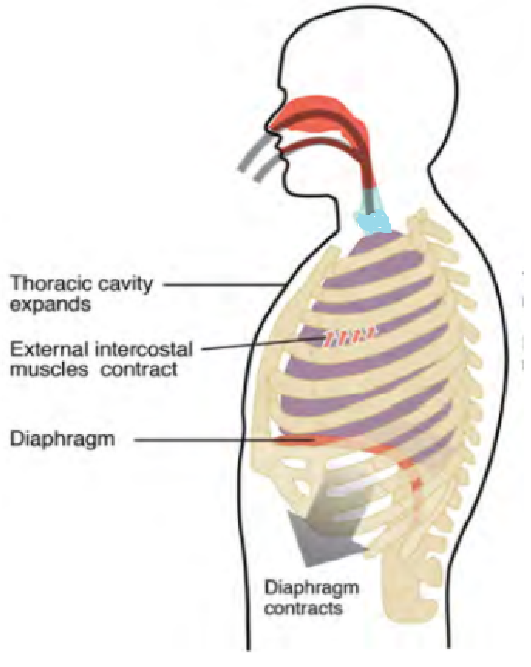
- Inspiration.
- Expiration.
- The following diagram represents mechanism of ----
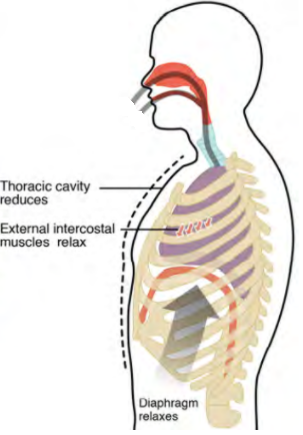
- Inspiration.
- Expiration.
- In the alveoli of the lungs, basement membranes of blood capillary and alveoli are fused with each other to form ----.
- Blood Membranes.
- Respiratory Membranes.
- Gaseous Membranes.
- Excretory Membranes.
- About 98% of oxygen in blood combines with Hemoglobin to form a complex called “-------”.
- Carboxyhemoglobin.
- Oxyhemoglobin.
- Carbaminohaemoglobin.
- Glycated Haemoglobin.
- The large concentration of CO2 (70%) reacts with water in RBC to form -------.
- Carbonic Acid (H2Co3).
- Carboxyhemoglobin.
- Oxyhemoglobin.
- Carbaminohaemoglobin.
- Some part of Co2 (20%) entered in RBC reacts with hemoglobin and forms a complex called “------”.
- Carbonic Acid (H2Co3) Complex.
- Carboxyhemoglobin.
- Oxyhemoglobin.
- Carbaminohaemoglobin.
- The amount of air that moves in and out of lungs during normal breathing is called “------”.
- Tidal Volume.
- Inspiratory Reserve Volume.
- Expiratory Reserve Volume.
- Residual Volume.
- The maximum amount of air that can be inhaled after normal inhalation is called “-------”.
- Tidal Volume.
- Inspiratory Reserve Volume.
- Expiratory Reserve Volume.
- Residual Volume.
- The maximum amount of air that can be exhaled after normal exhalation is called “-------”.
- Tidal Volume.
- Inspiratory Reserve Volume.
- Expiratory Reserve Volume.
- Residual Volume.
- The amount of air remaining in lungs after a forceful expiration is called “-------”.
- Tidal Volume.
- Inspiratory Reserve Volume.
- Expiratory Reserve Volume.
- Residual Volume.
- Sensory nerve fibers to lungs arise from the ------.
- Optic Nerve.
- Olfactory Nerve.
- Vagus Nerve.
- Glossopharyngeal Nerve.
Labels: Human Anatomy and Physiology
posted by Dr. Shirish Nagansurkar @ July 21, 2021



<< Home