- Leprosy is an infectious disease caused by a acid fast bacillus called as “Mycobacterium leprae”.
- Leprosy is called as “Kushtharog or Maharog” in India.
- This disease is present from ancient times but,the Gregor Hansen in 1873 discovered the causative organism as “Mycobacterium leprae” hence the disease is called as “Hansen’s Disease” also.
- The leprosy bacillus attacks the schwan cell nucleus in neuron and hence affects the peripheral nervous system and skin.
Signs of Leprosy:
- Leprosy is characterized by presence of patches on skin, the patches of leprosy are characterized by,
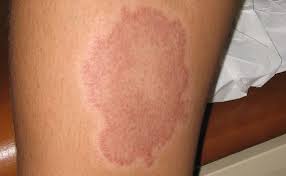
- Definite loss of sensation.
- Do not itch or hurt.
- hypopigmentation to reddish or copper red colored.
- No sensation of pain.
- May be flat or elevated.
Diagnosis of Leprosy:
- Leprosy patches can easily be identified by checking sensation in comparison to normal skin.
- Skin smear test for presence of bacterias.
Mycobacterium leprae:
- Its a acid fast bacillus and shows positive reaction to Zeil-Nellson Reagent test.
- This bacteria grows very slowly : Has incubation period of 5 yrs.
- This is the first bacteria discovered which is known to cause disease in humans.
- This bacterium was discovered by Gerhard Armauer Hansen in 1873.
- This bacteria can not be grown on artificial mediums, it has to be grown on certain lab animals like some species of monkeys, rats, armadillo and rabbits.
- Like Mycobacterium tubercles this bacteria is also known to produce resistance.
The drugs which are used in treatment of leprosy are called as “Antileprotic Drugs”
Classification:
1) Sulfones:
- Dapsone.
- Solapsone.
- Acedapsone.
2) Phenazines:
- Clofazimine.
3) Thiosemicarbazones:
- Amithiazone.
4) Antitubercular drugs:
- Rifampicin.
- Pyrazinamide.
- Ethionamide.
5) Antibiotics:
- Minocycline.
- Ofloxacin.
- Clarithromycin.
6) Natural:
- Chaulmoogra oil.
Dapsone
- Sulfones were first employed in treatment of leprosy in 1941, Dapsone is most favorable drug in the treatment of leprosy.

- Chemical name : 4-4 Diamino Diphenyl Sulfone.
Mechanism of Action:
- Dapsone is a bacteriostatic and acts by inhibiting folic acid synthesis of mycobacterium.
- It has similar mechanism like sulfonamides i.e. it inhibits bacterial folate synthtase and prevent formation of dihydrofolic acid from PABA.
- It also has significant anti-inflammatory action.
Structure Activity Relationship: SAR:
- Sulfone group is found essential for action as replacing it diminishes the activity.
- Replacement of benzene rings with thiazole rings produced “Thiazosulfone” which is found to be less active as compared to Dapsone.
- Replacement of one hydrogen from each amino group with acetyl group gave less active “Acedapsone” which is have less solubility and hence used for depot injections.
- Replacement of one hydrogen from each amino group with –CH2SO2, gave rise to Sulfomethonates, which are having lesser activity.

Adverse Effects / Side Effects of Dapsone:
- Gastric Irritation.
- Dermatitis.
- Anorexia.
- hepatitis.
- Psychosis.
Therapeutic Uses:
- In treatment of multibacillary (more than 5 patches) and paucibacillary (1 to 5 patches) leprosy in combination with other drugs.
- In combination with Pyrimethamine, Dapsone is used in prophylaxis of malaria.
- In certain inflammatory skin conditions like Polycondritis, leishminiasis etc.
- To treat pneumonia in AIDS with Trimethoprim
Clofazimine.
- It is a secondary drug that is used in combination with other drugs used in treatment of Leprosy.
- Chemically its a “Phenazine” derivative.
- its is water soluble red dye known to cause discoloration of skin (Hypopigmentation.), sweat, sputum, feces, eye lid lining, urine etc.
Mechanism of Action:
- The exact mechanism through which Clofazimine exerts its effect is unknown.
- However, it binds preferentially to mycobacterial DNA, thereby inhibiting DNA replication and cell growth.
- Clofazimine has a slow bactericidal effect on Mycobacterium leprae and is active against various other Mycobacteria.
- It is also known to enhance the cellular defense system.
Structure Activity Relationship:
- The “Phenazine” nucleus is found essential for Antimycobacterial and Immunosuppressive actions of Clofazimine.
- The halogen substitution at para position of phenyl groups at C3 and N10 found to increase the activity.
- The substitution at “imino” group is found to be essential as the substitution with alkyl and cycloalkyl groups increased the activity.
Adverse Effects / Side Effects:
- GI irritation.
- Change in color of skin.
- Darkening of body secretions.
- Scaly itchy skin.
Therapeutic Uses:
- It is a secondary drug used in treatment of leprosy in combination with other drugs.
- Its immunosuppressive action can be useful in treatment of many autoimmune diseases like sclerosis, psoriasis, type 1 diabetes etc.

