Definition & Importance of Size reduction
Size Reduction or Comminution is a pharmaceutical process where bigger drug particles are converted into smaller drug particle as per requirement.
Importance:
To increase the rate of a solution: Size reduction reduces particle size and increases effective surface area which in turn increases the rate of solution.
To increase the rate of extraction: Rate of extraction is directly proportional to Size reduction. Smaller particle size allows faster penetration of menstruum and hence fastens the extraction process.
Mixing: Smaller particle size ensures effective mixing which is an essential thing for many pharmaceutical dosage forms.
Bioavailability: As particle size decreases the rate of absorption increases. Hence size reduction ensures good bioavailability e.g Griseofulvin.
Drying: Reduction in particle size increases effective surface area and fastens the process of drying.
To facilitate Filtration: Rate of filtration depends upon the size of particles to be separated.
Stability: Reduction in particle size increases the stability of certain pharmaceutical preparations such as suspensions and emulsions.
Factors Affecting Size Reduction
Various factors which affect process of size reduction are as follows,
Hardness: It is easy to reduce the size of soft materials as compared to hard materials.
Toughness: The crude drugs having fibrous nature containing more moisture content are more difficult for size reduction than hard but brittle substances.
Stickiness: The gummy materials such as resins tend to adhere to grinding surfaces or sieves of the mill and produce a lot of problems during operation. In such cases complete drying of materials is useful.
Material Structure: Materials with a special structure such as plant materials and minerals with weakness lines produce fibers and flakes during operation and produce problems.
Moisture Content: The moisture content of material influence many properties like hardness, toughness, stickiness etc.. Usually 5% moisture in dry grinding and 50% moisture in wet grinding is considered good for size reduction.
Softening Temperature: The fatty or waxy drugs softens during the process due to heat generation by process and jams the mill. However, this can be avoided by employing a cooling mechanism in the mill.
Purity Required: The grinding surfaces of mills may wear off and appear in the final product and compromise the purity of final product. This can be avoided by proper selection of mills and cleaning of mill between batches.
Physiological Effect of Material: Some drugs are very potent, their dusting during operation may harm the operator this can be avoided by enclosing completely the mill.
Mechanisms of Size Reduction
Mechanisms of Size Reduction:
1) Cutting:
- The material is size reduced when it comes between sharp edges of the blades.
- e.g Cutter Mill.
2) Compression:
- The material is size reduced by crushing when comes between a stationary platform and a moving heavy platform.
- e.g. Mortar and pestle, Roller Mill.
3) Impact:
- The material is size reduced when hit by a moving platform or material at a high speed.
- e.g Dis-integrator, hammer mill.
4) Attrition:
- The material is size reduced by application of pressure and the shear force generated when it comes between the platforms moving relative to each other.
- e.g Mortar and pestle and Roller mill.
5) Combined Impact and Attrition:
- The material is size reduced by combined action of impact and attrition to get better results.
- e.g. Ball Mill, Fluid energy mill.
Cutter Mill:
Principle: Works on the principle
of cutting.
Construction:
- The mill consists of metallic body, feed, screen, set of blades, rotor, and a product outlet.
- The mill consists of two sets of blades, one is rotating and one is fixed to the body.
- The rotor moves with help of electricity.
- The speed of the machine can be adjusted with help of control mechanism.
- The base of the body contains a screen, the screens of different aperture size can be attached to get desired product size.
Working:
- The material to be size reduced is entered into the machine through a hopper.
- The electrical supply to the machine is started after a careful closure of the machine feed.
- The rotors are rotated at desired speed.
- The size reduction takes place when the material comes between rotating and fixed blade by a mechanism of cutting.
- The size reduced material falls on the screen present at the bottom.
- The vibration of mill helps in moving of product into the outlet.
- The size reduced material is collected from product outlet.
Advantages:
- Suitable for drugs of plant origin.
- Application of screen ensures the product of desired size range.
Disadvantages:
- Not suitable for sticky products.
- Produces heat hence not suitable for thermolabile substances.
Applications:
- For size reduction of crude drugs of plant origin.
Ball Mill
Principle: Works on the principle of Impact and Attrition.
Construction:
- The mill consist of a hollow cylinder fixed on metallic frame in such a way that it can rotate around its horizontal axis.
- The cylinder contains metallic balls occupying around 30 to 50% of total capacity.
- The balls are usually made up of rubber, porcelain or metal.
- The metallic balls are coated with chrome.
- The weight of balls is kept constant and size of balls depends upon the size of feed and mill.
Working:
- The material to be size reduced is entered into the machine through a hopper.
- The electrical supply to the machine is started after a careful closure of the machine feed.
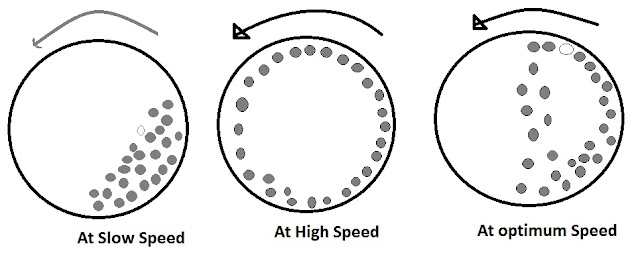
- The mill is rotated at optimum speed.
- For effective size reduction speed of machine plays a very important.
- If the machine is rotated at low speed the balls collide with each other and no or negligible size reduction takes place.
- If the machine is rotated at very high speed the balls rotate along the cylinder wall due to centrifugal force and no size reduction take place.
- If machine is moved at an optimum speed (two third speed)
- Size reduction takes place as balls move at the top and fall down crushing the material by impact and attrition.
- After sufficient time the mill is stopped and product is collected.
Advantages:
- One of the most efficient mills can produce very fine powders.
- Suitable for both wet and dry grinding.
- As operation takes place in a closed environment the mill is useful for potent materials.
- The mill after some modifications is useful for continuous operation.
Disadvantages:
- Not suitable for sticky products.
- Very noisy.
- Balls and casing material may wear off and can compromise the purity of product.
Applications:
- Useful for a variety of materials to produce fine powders.
Fluid Energy Mill / Micronizer:
Principle: Works on the principle of Combined Impact and Attrition.
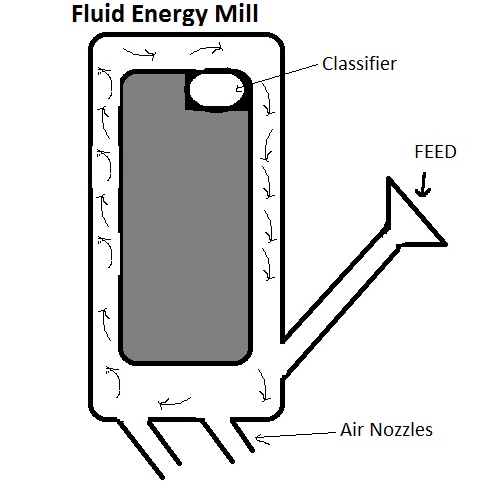
Construction:
- It consists of a loop of metallic pipe with a diameter of 20 to 200 mm depending on the height of loop, which may be around 2 m.
- It has an opening for material feed.
- The base of the mill has nozzles for inlet of air under pressure.
- The mill at the top has an opening with a classifier which acts as a product outlet.
- Most of the time the outlet is connected with Cyclone Separator for size separation of particles.
Working:
- The material to be size reduced is entered in the machine through the feed.
- The nozzles at base introduce the air under pressure at high velocity which pushes the particles towards the wall.
- The material moves in an elliptical path creating turbulence.
- The size reduction takes place due to the impact of particles on the wall and inter-particulate friction.
- The smaller particles are carried away with air at the top while the larger particles due to centrifugal force are throw at the bottom and again get thrown away till becomes small in size.
- Other inert gasses can be used as per requirement of material.
- The expanding and moving of air also cools down the heat generated by the mill.
- The particles of desired size range get separated by classifier while others continue their journey with air flow.
- Fluid energy mill is considered as one of the most efficient mills as it can produce particles up to 1 to 20-micron size.
Advantages:
- Produces very fine particles.
- Useful for heat sensitive materials.
- Classifier provides desired size product.
- Continuous operation is possible.
- No wear and tear: no contamination.
- Verity of size is available as per the need of industry.
Disadvantages:
- Not suitable for sticky products.
Applications:
- To produce very fine particle at a large scale.
Disintegrator:
Principle: Works on the principle of Impact.
Construction:
- The mill consists of a metallic body with an inner undulating surface, feed, screen, set of beaters, rotor, dust bag and a product outlet.
- The inner surface is undulated which facilitates size reduction.
- The mill consists beaters attached to a rotor.
- The rotor moves with help of electricity.
- The speed of the machine can be adjusted with help of control mechanism.
- The dust bag is attached to remove dust generated during operation.
- The base of the body contains a screen, the screens of different aperture size can be attached to get desired product size.
Working:
- The material to be size reduced is entered into the machine through the hopper.
- The electrical supply to the machine is started after a careful closure of the machine feed.
- The rotors are rotated at desired speed.
- The size reduction takes place by mechanisms of impact when material falls on the beater and is thrown on an undulating inner surface, the process repeats.
- The size reduced material falls on the screen present at the bottom.
- The dust generated during operation is collected in the dust bag.
- The vibration of mill helps in moving of product into the outlet.
- The size reduced material is collected from product outlet.
Advantages:
- Useful for batch operations.
- Application of screen ensures the product of desired size range.
Disadvantages:
- Not suitable for sticky products.
- Not useful for a continuous process.
- Produces heat hence not suitable for thermolabile substances.
- Pretreatment of material is necessary before the operation: Adds to cost of the final product.
Applications:
- To powder very hard drugs.
- As application takes place in closed environment useful for potent drugs also.
Hammer Mill:
Principle:
- Works on the principle of Impact.
Construction:
- The mill consists of a metallic case, rotor, a central shaft with hammers, screen, feed and outlet.
- The metallic case contains a rotor at the middle which has attached four to seven swinging hammers.
- The motor is moved with help of electricity and speed of which can be controlled with help of panels.
- The feed is used to introduce raw material in the mill.
- The removable screen is attached at the bottom.
- The product outlet at the bottom is used to collect finished product.
Working:
- The material to be size reduced is introduced into the mill through the feed.
- The electrical supply of mill is started after a careful closure of feed.
- The central panel with hammers starts rotating at speed.
- The size reduction takes place when material his hit by swinging hammers and collision of particles with the stationary metallic wall of the case.
- The size reduced material falls on the screen at the bottom.
- The vibrations of mill help in coming out of product through the screen.
- The screen of desired aperture size can be used as per requirement.
Advantages:
- Useful for hard substances.
- Suitable for continuous operation after simple modifications.
Disadvantages:
- Not suitable for sticky substances like resins.
- Produces heat hence not useful for heat sensitive substances.
Edge Runner Mill:
Principle:
It works on the principle of Crushing and Attrition.
Construction:
Also known as Chilean mill or Roller stone mill.
It consists of one or two heavy steel or granite rollers mounted on a horizontal shaft and turned round a central vertical shaft on a bed of steel or granite.
The stones may vary from 0.5 to 2.5 m in diameter, the larger size weighing up to about 6 tonnes.
Working:
The material to be ground is kept in the path of the runner by scrapers.
The reduction is partly due to crushing: by the weight of the stones, but more to friction between the surfaces of contact between the runners and the bed stone.
Application:
Edge runner mills are gradually being replaced by more sophisticated machines.
Used particularly for reducing extremely tough and fibrous materials – roots and barks to the form of powder.
End Runner Mill:
Principle:
It works on the principle of Crushing and Attrition.
Construction:
It consists of a weighted pestle mounted eccentrically in a ceramic, granite or metal mortar, which is rotated by a motor.
The pestle rotates by friction and is free to rise and fall in the mortar so that its grinding action involves both impact and shear, the material being crushed and rubbed between it and the rotating mortar.
Spring-loaded scrapers ensure that material is constantly returned to the grinding area and at the end of the operation the pestle can be swung clear of the mortar to facilitate emptying and cleaning.
Working:
Pastel is moved up and the material to be introduced is introduced into the morter.
The pastel is lowered and the electric supply of the mill is started.
The material is crushed under the weight of pastel, the rotation of the pastel causes size reduction by attrition as particles are crushed and moved under shear force between pastel and bed wall.
The scrapper helps keep the material in the path of the pastel.
Once size reduction is done the pastel is moved upwards, the product is collected and the mill is washed dried and kept ready for next operation.
Advantages:
Produces moderately fine powder.
Useful for fibrous products like leaves and roots.
Wet grinding with very viscous material such as ointments and paste is also possible.
Disadvantages:
Not useful for sticky products.
Potency can be compromised.
Open operation.
Wear and Tear.